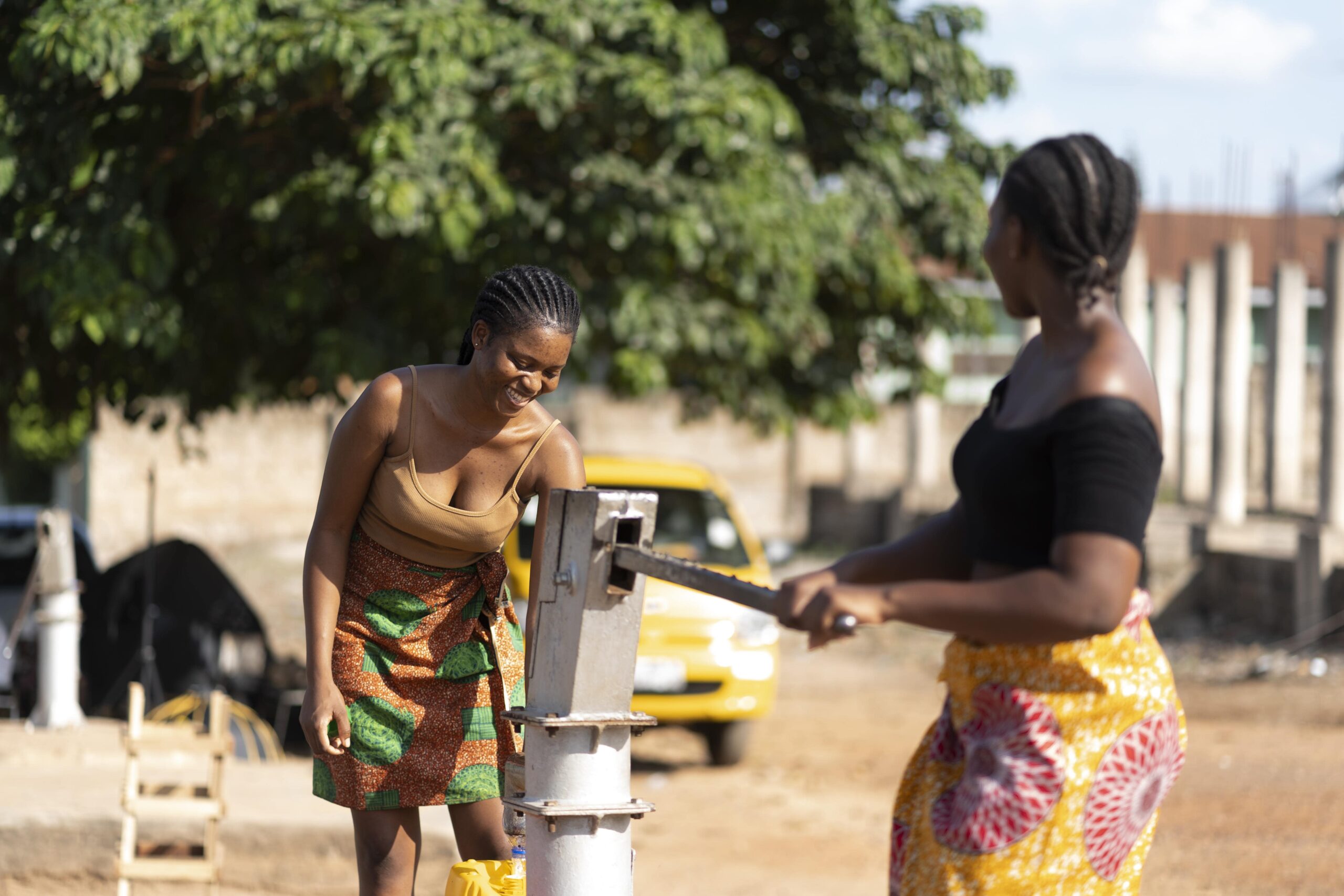Water is the lifeblood of our planet. Every living organism, from the tiniest microorganism to the largest mammal, relies on water for survival. Yet, despite its fundamental importance, the world is facing an escalating water crisis that threatens to affect every corner of the globe. Understanding the global water crisis and how it affects us all is crucial for taking steps to mitigate its impact and ensure a sustainable future.
The Scope Of The Water Crisis
The global water crisis is multifaceted, encompassing issues of scarcity, quality, and accessibility. According to the United Nations, nearly 2.2 billion people worldwide lack access to safe drinking water. This figure represents almost one-third of the global population, highlighting the severe and widespread nature of the crisis.
Scarcity is a major component of the water crisis. While water covers approximately 71% of the Earth’s surface, only about 2.5% of this water is freshwater, and just a fraction of that is accessible for human use. As populations grow and demand for water increases, the available supply is stretched thinner, leading to significant shortages in many regions.
Quality is another critical issue. Pollution from industrial, agricultural, and urban sources contaminates water supplies, making them unsafe for consumption. In many developing countries, untreated wastewater is discharged directly into rivers and lakes, exacerbating the problem and leading to severe health consequences for local populations.
Accessibility to water is also a significant challenge. In many parts of the world, people, particularly women and children, spend hours each day traveling long distances to collect water. This not only reduces their quality of life but also limits opportunities for education and economic advancement.

How The Water Crisis Affects Us All
The impacts of the global water crisis are far-reaching, affecting not just those in water-scarce regions but also the global community at large.
Health And Well-being: Lack of access to clean water leads to numerous health problems. Waterborne diseases such as cholera, dysentery, and typhoid fever are prevalent in areas with contaminated water supplies. These diseases can be fatal, especially for children and the elderly. Furthermore, inadequate water for hygiene exacerbates the spread of illnesses, creating a vicious cycle of poor health and poverty.
Food Security: Agriculture is the largest consumer of freshwater, accounting for about 70% of global water withdrawals. Water scarcity directly impacts food production, leading to lower crop yields and higher food prices. This can result in food shortages and malnutrition, particularly in vulnerable communities. As the global population continues to grow, ensuring sufficient water for agriculture will be crucial for maintaining food security.
Economic Impact: Water is essential for many industries, including manufacturing, energy production, and tourism. Water shortages can disrupt these sectors, leading to economic losses and job insecurity. In addition, the costs associated with addressing water pollution and scarcity place a significant financial burden on governments and communities.
Environmental Degradation: The over-extraction of water from rivers, lakes, and aquifers can lead to environmental degradation. Wetlands, which provide critical habitat for wildlife and act as natural water filters, are particularly vulnerable. The loss of these ecosystems can have cascading effects on biodiversity and the health of the environment.
Conclusion
The global water crisis is a complex and pressing issue that affects us all. By understanding its causes and impacts, and by taking collective action to address it, we can work towards a future where everyone has access to the clean, safe water they need to thrive. It is our shared responsibility to ensure that this vital resource is protected and preserved for generations to come.